A Complete Guide to Systematic Random Sampling: Key Insights and Examples
In a study, it is important to pick a representative sample of a large population. Systematic random sampling is one of the most effective ways of doing this. This method relies on a constant, periodic time period to select the participants and that is why it is simple and effective, particularly when dealing with large sample sizes.
Here we are going to explore the basics of systematic random sampling, how it functions and the reasons behind its usefulness as a researcher tool.
What is Systematic Random Sampling and How Does It Work?
Systematic random sampling is a form of probability sampling whereby all the members of a population are given equal probability to be chosen but in an organized fashion.
The method does not pick the participants at random but uses a pre-determined and periodic duration to pick participants.
This will start with the identification of the intended sample size. After determining the sample size, the other thing that is done is to compute the sampling interval which is by dividing the population size with the sample size.
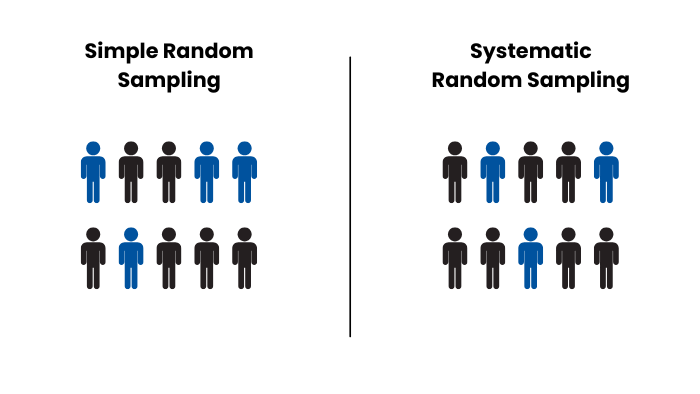
How Does Systematic Sampling Compare to Simple Random Sampling?
While both methods are used to ensure randomness, they are fundamentally different in how they select participants.
Simple Random Sampling:
- Everybody has an equal chance of being chosen, and the choice is made at random.
- It needs a full list of population and random selection techniques (random number generators).
Systematic Random Sampling:
- The participants are chosen according to a set time interval.
- When the starting point has been selected, the process proceeds in a predetermined, regular manner.
Which One to Use?
- Simple random sampling can be more flexible, but it may be difficult to implement in large populations.
- Systematic random sampling is ideal for large datasets and ensures efficient data collection.
What Are the Types of Systematic Sampling?
There are various ways in which systematic sampling can be conducted and this is based on the requirements of the research study.
Linear Systematic sampling:
Linear Systematic sampling and the circle sampling are the most prevalent ones. In the linear systematic sampling, the researchers will pick the participants in a straight line at the fixed intervals.
The process is stopped when the list of the participants is exhausted, and every participant has a similar chance of being selected. The technique is normally applied in large scale surveys or research studies where a non repetitive but predictable selection process is needed.
Circular systematic:
Circular systematic sampling on the other hand is a bit different.
In this technique, when the end of the list is reached, the process of selection will restart with wrapping around the end. This guarantees that the whole population has been sampled even when the number of participants is not a multiple of the sample size.
Circular sampling is best used where the population list cannot be divided proportionately by the required sample size to provide a balanced distribution throughout the entire population.
Why Should You Choose Systematic Random Sampling Over Other Methods?
You can use systematic random sampling because there are a number of reasons why it is the ideal sampling method in your study. Its ease of implementation is one of the largest merits. In contrast to simple random sampling where complex random sampling mechanisms are needed in the technique, systematic sampling has a simple and predictable process.
This is particularly advantageous in cases where researchers have to work with a big sample of population or have time/resource constraints. A second reason to use systematic random sampling is that it is cost effective. Due to the efficiency and organization of the sampling process, it is time and resource saving, which is essential in the case of limited budgets or strict deadlines.
Moreover, systematic random sampling also contributes to the minimization of the bias. It removes any possibility of a human error or a subjective approach to selection since the time interval is predefined, and thus the sample is chosen in a fair manner.
Finally, the predictability and control of this approach provide peace of mind too. Although the beginning point is random, the remaining part of the selection process is based on a predetermined pattern, thus, researchers can rely on the fact that their sample is representative and reliable.
When Should You Use Systematic Sampling in Your Research?
Systematic random sampling works best when you need a simple and efficient way to collect data from a large population. It’s especially useful when:
- The Population size is known: You can calculate the interval accurately.
- You Have a List of Participants: An organized list of your population makes the process easier.
- You Have Budget or Time Constraints: The method is more cost-effective and quicker than simple random sampling.
What Are the Risks and Limitations of Systematic Random Sampling?
Although effective, systematic random sampling has some potential drawbacks to be aware of:
Bias with Ordered Data:
- You can unintentionally bias the population sample in the case there is some underlying pattern in the list of population (e.g., a collection of genders or ages).
Population Size Uncertainty:
- The procedure needs the awareness of the overall population size which may be a constraint when one is unaware of the population size. Yet, you may take an informed guess to continue with the sampling.
How Can You Perform Systematic Random Sampling Step-by-Step?
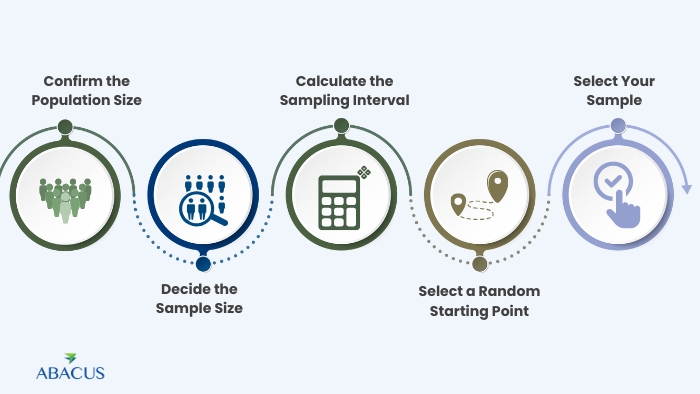
Performing systematic sampling is simple. Follow these steps to get started:
- Confirm the Population Size: Know how many participants are in your population.
- Decide the Sample Size: Determine how many individuals you want to include in your sample.
- Calculate the Sampling Interval: Divide the population size by the sample size to get the interval.
- Select a Random Starting Point: Choose a random number between 1 and your sampling interval.
- Select Your Sample: Begin with your random starting point and then select every nth individual (based on your calculated interval).
What Are Some Real-World Examples of Systematic Sampling in Action?
Systematic random sampling is a very useful method, and its usage is very widespread. In the example of the customer feedback surveys, companies tend to use systematic sampling to pick every 10th customer on their list and with this method; they have a representative sample but do not have to contact all of them. This approach ensures a manageable and unbiased sample for studying traffic patterns or vehicle behavior.
Conclusion:
Systematic random sampling is an effective instrument of collecting data about a large population in an effective and objective way. This approach makes the sampling process less cumbersome and at the same time, the results are accurate because the subjects are chosen at regular intervals. You can use systematic random sampling to get a reliable data whether you are doing a survey, research study or customer feedback session, provided that you do it in a fast manner.